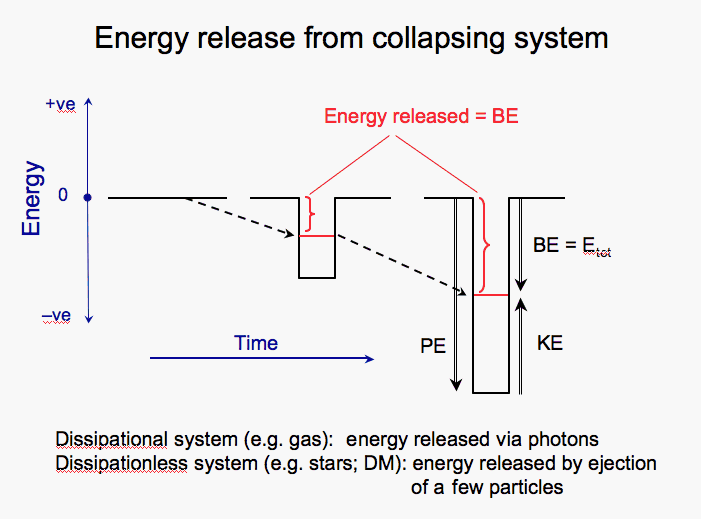
An initially highly diffuse system with stationary stars has nearly zero energy (no gravitational or kinetic energy). If it collapses, it's gravitational energy energy is converted to kinetic energy, so initially the total energy is still zero. However, when the system virializes, and energy is shared between the stars, then the final system is bound, with negative net (binding) energy. As a result, this binding energy must be released from the system. For gases this emerges as photon luminosity; for stellar systems, some stars are ejected above the escape speed and leave the system.