Gray-Scott Model at F 0.0140, k 0.0550
These images and movie demonstrate the behavior of the Gray-Scott reaction-diffusion system with σ=Du/Dv=2 and parameters F=0.0140, k=0.0550.
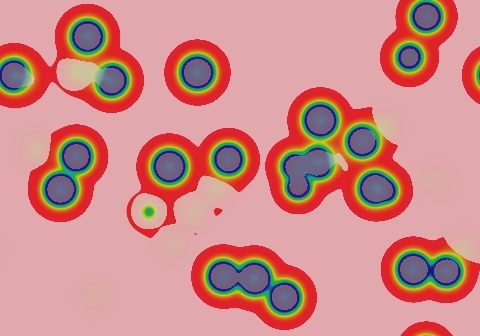
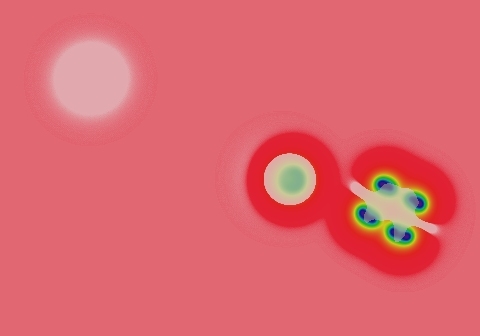
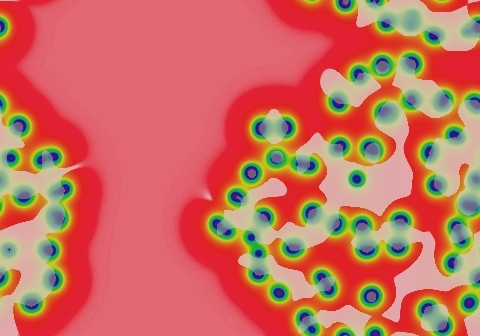
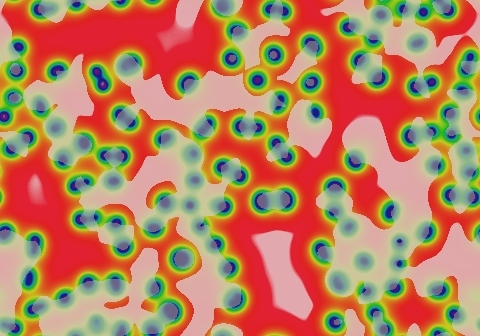
Symmetrical spots grow for a bit but die out immediately; asymmetrical spots survive by splitting into two smaller asymmetrical spots. The result is mostly "C" shapes that split into two smaller "C"s, with the viable portion at the end that is more sharply curved. As seen here, a suitable starting pattern can completely fill the space.
Categories: Pearson ε; Wolfram 3 (glossary of terms)
 increase F increase F
 | |||
 decrease k  |

|
15 frames/sec.; each fr. is 26 iter. steps = 13 tu; 1800 fr. total (23,400 tu) |  increase k 
|
|
| ||

 |
In these images:
- Color indicates level of u, ranging from purple (lowest u values) through blue, aqua, green, yellow and pink/red (highest u values)
- Areas where u is increasing are lightened to a light pastel tone; where u is decreasing the color is vivid.
- In areas where u is changing by less than ±3×10-6 per tu, an intermediate pastel color is seen. This includes areas that are in steady state or equilibrium.
''tu'' is the dimensionless unit of time, and ''lu'' the dimensionless unit of length, implicit in the equations that define the reaction-diffusion model. The grids for these simulations use Δx=1/143 lu and Δt=1/2 tu; the system is 3.2 lu wide. The simulation meets itself at the edges (periodic boundary condition); all images tile seamlessly if used as wallpaper.
Go back to Gray-Scott pattern index
This page was written in the "embarrassingly readable" markup language RHTF, and was last updated on 2019 Jan 05.
 s.11
s.11