Radar Antenna Engineering
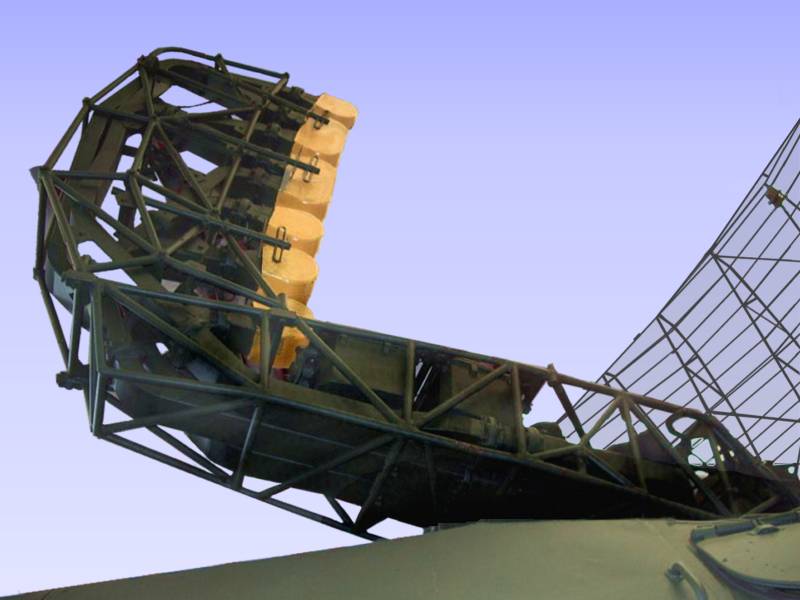

Figure 1: Arrangement of the feed horns of the Russian radar P-40 (NATO-designator: “Long Track”)
Figure 1: Preview of internet representation

Figure 1: Arrangement of the feed horns of the Russian radar P-40 (NATO-designator: “Long Track”)
Radar Antenna Engineering
An antenna is a structure that serves as a transition between wave propagating in free space, and the fluctuating voltages in the circuit to which it is connected. An antenna either receives energy from an electromagnetic field or radiates electromagnetic waves produced by a high-frequency generator. This section deals specifically with antennae used in radar installations.

Figure 2: Arrangement of the feed horns of the Russian radar P-40 (NATO-designator: “Long Track”)
Learning objectives:
The learning objectives serve as a preview of the information you are expected to learn in the chapter. This chapter provides the basis for understanding the specific radar antennae. Upon completion of this chapter, the student will be able to:
- describe antenna directivity and power gain characteristics;
- describe the focusing action of a basic parabolic antenna;
- describe the basic radiation patterns of the most common parabolic reflectors;
- describe the basic characteristics of horn radiators;
- describe the monopulse antennae concept.
Hint: If you want to use some pages of this home page as printed version, please have a look on the print preview of this preamble and check to use it as cover for your own printing version. Alternatively, you can use the applicable PDF-version of this chapter:
![]() Antennae Techniques - Book 3, “Radar Antennas”, (16 pages, 1112 kByte)
Antennae Techniques - Book 3, “Radar Antennas”, (16 pages, 1112 kByte)
