MIMO Radar Systems
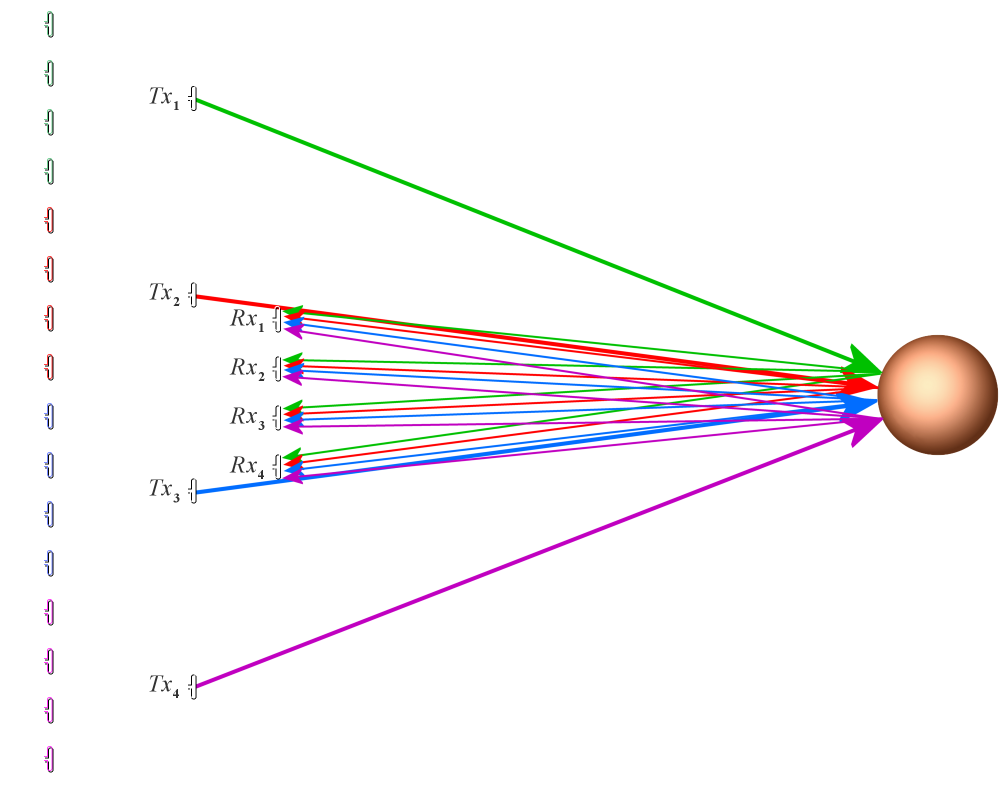
Figure 1: Principle of a MIMO radar system
In a MIMO system, the transmitting signals from the single transmitters are different.
As a result, the echo signals can be re-assigned to the source.
This gives an enlarged virtual receive aperture.
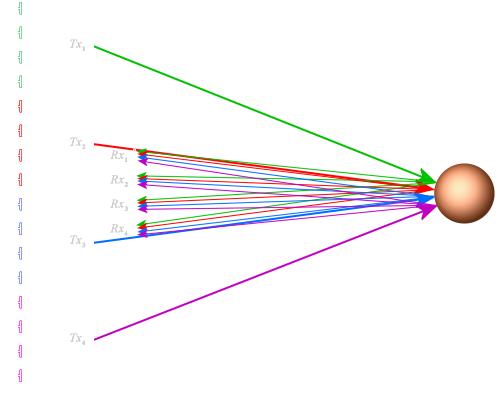
Figure 1: Principle of a MIMO radar system
In a MIMO system, the transmitting signals from the single transmitters are different.
As a result, the echo signals can be re-assigned to the source.
This gives an enlarged virtual receive aperture.
What is MIMO-Radar?
MIMO Radar Systems
MIMO radar system is a novel radar method in which MIMO stands for Multiple Input Multiple Output. It is a system of multiple antennas. Each transmit antenna radiates an arbitrary waveform independently of the other transmitting antennas. Each receiving antenna can receive these signals. Due to the different waveforms, the echo signals can be re-assigned to the single transmitter. From an antenna field of N transmitters and a field of K receivers mathematically results in a virtual field of K·N elements with an enlarged size of a virtual aperture.
MIMO radar systems can be used to improve the spatial resolution, and they provide a substantially improved immunity to interference. By improving the signal-to-noise ratio, the probability of detection of the targets is also increased.
The MIMO radar systems can be classified into two categories:
- MIMO radar with collocated antennas (so-called “Mono-Static” MIMO)
The target is a point target as in traditional radar systems. - MIMO radar with widely separated antennas (so-called “distributed” or “Bi-Static” MIMO).
The target is regarded by each antenna from another aspect angle.
“Mono-Static” MIMO
In the collocated radar case, the transmitting antennas are close enough such that the target radar cross-sections (RCS) observed by the transmitting antenna elements are identical. This system is similar to a thinned array of a phased array antenna in which each radiator has its own transceiver module and its own A/D converter. However, in a phased array antenna, each radiator only transmits (possibly time-shifted) a copy of a transmission signal, which has been generated in a central waveform generator. In a MIMO radar system, each radiator has its own arbitrary waveform generator and subsequently, each radiator uses an individual waveform. This individual waveform is also the basis for an assignment of the echo signals to their source. If in publications are compared MIMO and phased array then the phased array antenna is often depicted as SIMO (Single Input Multiple Output).
“Bi-Static” MIMO
In the distributed arrangement of the antennas, the radar data processing is much more complex. In contrast to “Mono-Static” MIMO, each radar antenna looks at the target from a different aspect angle. Therefore the target provides a different radar cross-section for each radar antenna. This requires much more complex target models for radar data processing.
Reference:
- Jian Li (Ph. D.): “MIMO Radar Signal Processing” Wiley-IEEE Press, 2009, ISBN 9780470178980
