Plot Processor
Radar channels A & B
of short pulses
of long pulses
(high beam)
of long pulses
(low beam)
combination
Figure 1: Block diagramm of a plot processor in a frequency-diversity radar using high- and low-beam feeding of the antenna
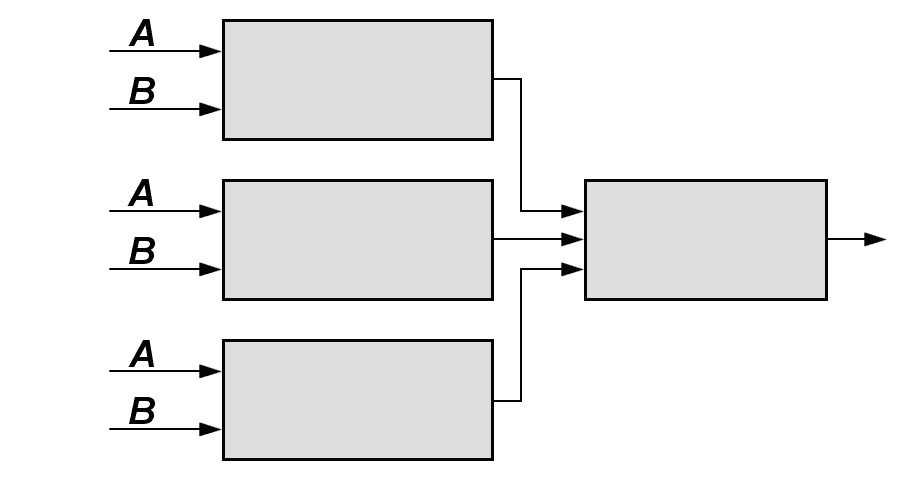
Radar channels A & B
of short pulses
of long pulses
(high beam)
of long pulses
(low beam)
combination
Figure 1: Block diagramm of a plot processor in a frequency-diversity radar using high- and low-beam feeding of the antenna

Radar channels A & B
of short pulses
of long pulses
(high beam)
of long pulses
(low beam)
combination
Figure 1: Block diagramm of a plot processor in a frequency-diversity radar using high- and low-beam feeding of the antenna
Plot Processor
The principal role of the plot processor is to combine primary plots from the various primary radar channels or sources into a single best estimate plot. The plot processor may also incorporate a range of other functions to improve the quality of the primary radar plot. A typical modern primary radar will generate plots from some or all of the following:
- each radar channel can produce plots
- multi-pulse working can produce plots from each of the pulses (e.g. short and long pulses)
- frequency diversity produces plots from each of the frequencies (frequency diversity can be implemented within one channel or utilising two channels)
- separately processed high and low beams.
In general the combination of information from all these sources is best carried out at plot level. Combining data earlier in the system usually involves loss of information, particularly, if carried out before coherent integration. Plot combination can be carried out in a general purpose computer which permits full control of the characteristics of the combination process. Typically, the plot combination will include a weighted average of position of the related plots modified by other parameters such as the energy level.
